Shared:2019Concept
Off-Earth Manufacturing and Construction (of Habitats)
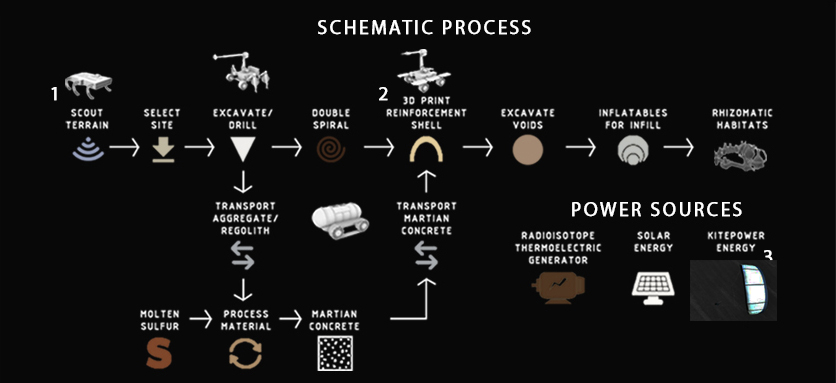
Process
Excavation and inflatable structure
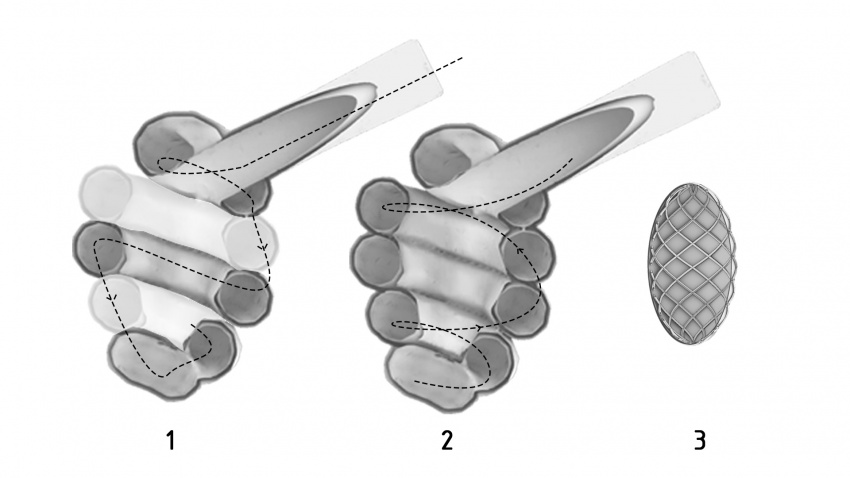
1. First phase of robot-aided, downward progressing excavation and gradual tunnel reinforcement using 3D printing.
2. Completion of excavation in upward movement.
3. Pressurized inflatable (as for instance https://www.extremetech.com/extreme/297081-aerospace-firm-shows-off-giant-inflatable-space-habitat) for the living environment is placed in the created cavity between the spiraling tunnels.
Reference: Inflatable Structure for Space- PDF Link
 Fig.1: In-situ progress of excavation and preparation of inhabitable spaces
Fig.1: In-situ progress of excavation and preparation of inhabitable spaces
Melissa Life Support System - a conversation with Robert Lindner and Christel Paille from ESA
The Melissa system is a unique and indispensable tool for space exploration. It ensures a reliable support of vital functions during the flight with potential use for Off-Earth Habitats. We have talked with Robert Lindner and Christel Paille from ESA ESTEC about the integration of this system in our Mars habitat, about the LSS itself and their vision for the future. Following here is a series of topics discussed:
Q: Is it possible to operate Melissa on an economy-system, for instance shut it off for one of the three inflatables it is connected to?
A: The Life Support System is designed to operate at its maximum capacity corresponding to the volume of the habitat it has been designed for. Although this system can be adaptable to different inputs (for instance the metabolism of humans changes during the night), it is preferred not to have accumulations (high inputs and low outputs).
Q: What are the possibilities of scaling up the system? And the challenges?
A: The current capacity of the Melissa prototype for experiments corresponds to the oxygen consumed by one human. We are currently looking into the possibilities of scaling up the system. Because it is based on biochemical processes, the scaling would not be happening in a linear manner (increase in one compartment might cause a three-fold increase in another). Also, regarding the astronauts needs in terms of food, the diet is based on animal input, which currently is more feasible to be provided from Earth.
Q: How much of a Melissa system could be created with materials on site? What is the possibility of the use of regolith/water from the Martian surface?
A: Currently Melissa has a membrane for processing the recycling of grey water. If we think about oxygen, this could be obtained through either electrolysis or classical chemical reduction processes. The regolith on Mars has substantial amounts of oxygen, and if the regolith would be processed for obtaining oxygen, a side effect of this process is obtaining metals as well through the extraction. The challenge is that this process would necessitate complex industrial facilities and considerable amounts of energy. Furthermore, one important implication of supplying resources such as on-site extracted water from ice is the insuring and monitoring of water quality, which does currently take place by ISS within a closed habitat.
Q What is the current capacity of Melissa LSS (in terms of oxygen/water/waste) and how close/far does this system need to be located to the living environment that it serves?
A: Currently the pilot installation in Barcelona is able to recycle 100% of oxygen, water, bio-waste. Provided there is a reliable distribution infrastructure, there is no reason why it should be too close to the system. One idea would be to have a central hub that distributes resources to all the habitats.
Q: What is the degree of redundancy of such a system (imagine loss of insulation capacities of the inflatable/accident)?
A: Operating with a no redundancy or even single redundancy is not an option for the Melissa system. It operates on a redundancy level by which at every moment two systems are working in parallel. In case one of them stops working, the other takes over. Regarding the possibility of an accident such as a fire inside the inflatable, the space must be evacuated and isolated, first extinguishing the fire, switching off the ventilation system, making sure smoke does not spread around and that no more oxygen is coming in.
We are excited to stay in touch with the development of the Melissa system, realizing that the dialogue between the technical development of such a system and its architectural purpose, namely human life support for off-Earth habitats, will be essential.
https://www.esa.int/Enabling_Support/Space_Engineering_Technology/Melissa/Closed_Loop_Compartments
3D printing approach
3D printing using swarm of rovers has been explored for a project on Earth (http://100ybp.roboticbuilding.eu/index.php/project02:ROBOTIC-PRODUCTION) and could be envisioned to be implemented similarly off-Earth.

Anim. 1: 3D printing swarm of rovers
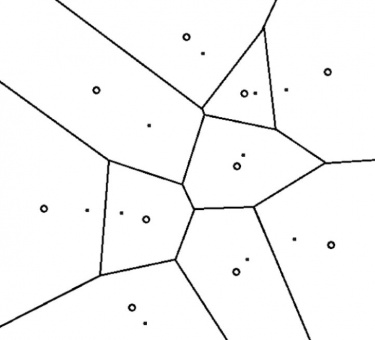
Adaptive 3D Voronoi approach
Fig.2: Voronoi principle (left) and 3d application (right)
For spatial allocation at neighborhood scale we considered using the Voronoi logic. The advantages would be:
1. Extension of neighboring living areas.
2. Economy of resources due to less excavation (shared connection tunnels, shared material).
3. Possible organizational model for internal subdivision of space.
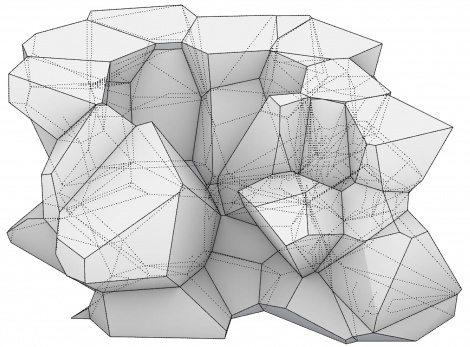
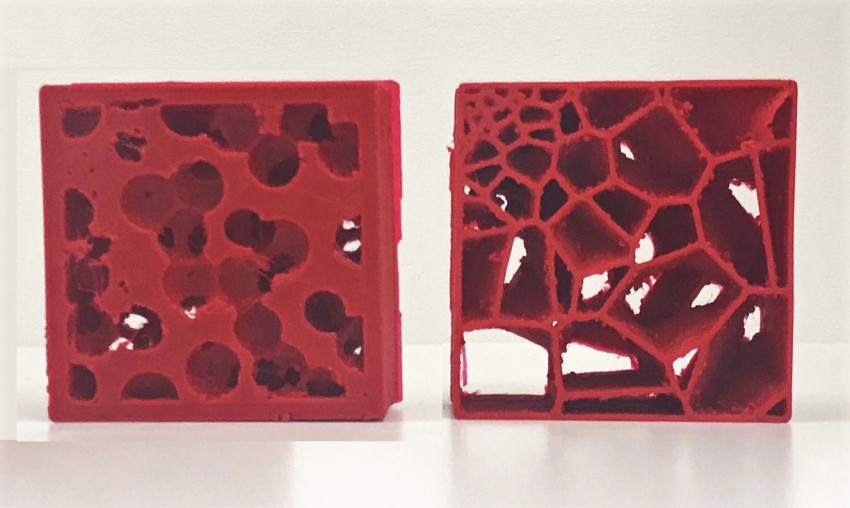 Fig.3: 3D-printed Voronoi applications
Fig.3: 3D-printed Voronoi applications
Robotic Production
Professor Angelo Vermeulen on the social and psychological implications of living in space.
The following are extracts from a dialogue with professor Angelo Vermeulen from TU Delft, space system researcher and biologist. Prof. Vermeulen shares his experience in leading one of the analogue space missions in Hawaii as crew commander and the impact confinement has on the psychology of the astronauts. The period of this mission was 4 months, but professor Vermeulen has participated in various other isolation experiments with the purpose of understanding human life in space.
"Mission restrictions:
1. Limited space and reduced privacy (living in a dome with diameter of 11 meters). Everything is there: lab, kitchen, workspace, exercise space, small private rooms.
2. Isolated, no more real time communication with the outside. The only way you can communicate is by emails that are delayed: every email sent is delayed 20 minutes and every reply get delayed by 20 minutes, which is the max delay you would have on real Mars.
3. Proper water supply, was limited. We had access to a few very quick showers. I didn’t shower for a full month, instead using wet wipes and disinfecting liquid.
4. No fresh food, only shelf stable food supplies. Resupplies were possible if needed, but it was as if a cargo landed on Mars. A truck would deliver a cargo far away from our habitat, we would get a message, put on our space suits and would pick up the package. That simulated something arriving from Earth.
5. Habitat is a pretty open floor plan – gives the impression that things are spacious. You are in touch with each other, you don’t hide away from each other. You can reorganize the space according to what you need. Sometimes it becomes a workspace, a sports space – the space is flexible.
6. Diverse crew space. Culturally different backgrounds. The diversity made the experience very interesting – engaging conversations, different troubleshooting. If we move forward with space exploration, we need to bring in more women.
7. A bedroom – tiny room with no window, but the little space you have in that room is much appreciated, if you are living like this.
8. Only one porthole window through which to look outside.
9. EVA (Extravehicular activity) – going outside. We had to wear space suits (space suit simulators) – they inhibit your movements and isolate you from the outside air. So basically during all these months of isolation you don’t have any direct contact with fresh air. Most of these missions were set to study local geology and geological history.
We spent our days mostly doing all types of research, but the main study we were doing was a food study.
Space food is much richer nowadays, and astronauts are much happier about it (for instance tortillas are the most favorite food items on the space station because astronauts can customize the tortillas a little). However the problem of menu fatigue is real (it is also experienced by soldiers in the military – by eating the same food over and over again, you start eating less), and you don’t want skinny astronauts undernourished to arrive to Mars. We tried to come out with a solution. Challenges: food needs to be preserved in an easy way (no fridges), as light as possible, contain a lot of calories and be healthy and diverse. We were the crew allowed to prepare our own meals starting from ingredients (shelf-stable): 2 days of astronaut foods. The idea is that if you allow astronauts to cook their own food that would eliminate menu fatigue.
Other psychological and social aspects of HI-SEAS
1. Phenomena experienced: the fact of confinement starts to wave you down. In the second half of the mission, I started thinking that when I will be out of there I would be happy to just be in a room and able to open the door at any given moment.
2. The sense of warping of time, difficult to describe. We normally have a rich source of input from morning to evening, but on space missions we miss all the clues we have in daily life. Everything that happens is similar to other events and limited. That causes that our memory about what happened last week or two weeks ago to blur out. Time is running at a different speed.
3. Sleep quality goes down. Any time astronauts are in isolation, they develop sleep issues.
4. I was a commander. It was crucial to keep the crew together.
5. The biggest challenge, quite unexpected, was keeping communication with mission control in order. They were discussions, fights with mission control, from the beginning of ISS. On Mars astronauts’ reaction to the requirements of Mission Control could be: “why are you telling this, you’re not here, you don’t know”. This happens very easily. When you live in isolation you put everything under the microscope. So you read this email and maybe the person who wrote it was just being very quick and you analyze every sentence and think: oh, that’s quite a nasty way to put it. The whole crew gets a bit armed, and the person says: oh, I didn’t intend it this way."
As professor Vermeulen concluded, "going to Mars will probably be less a situation of lab performing experiments but more of a human experience."
Experiments with ice caps as insulation medium from radiation
Keywords
Inflatable, ice cap, pressurization, radiation shield.
Abstract
The discovery of water ice immediately under the surface of Mars by NASA’s Phoenix lander in 2008 prompted in our team an idea. Due to the very thin atmosphere surrounding the planet, an inhabited space needs good shielding from radiation. Solid water presents an opportunity.
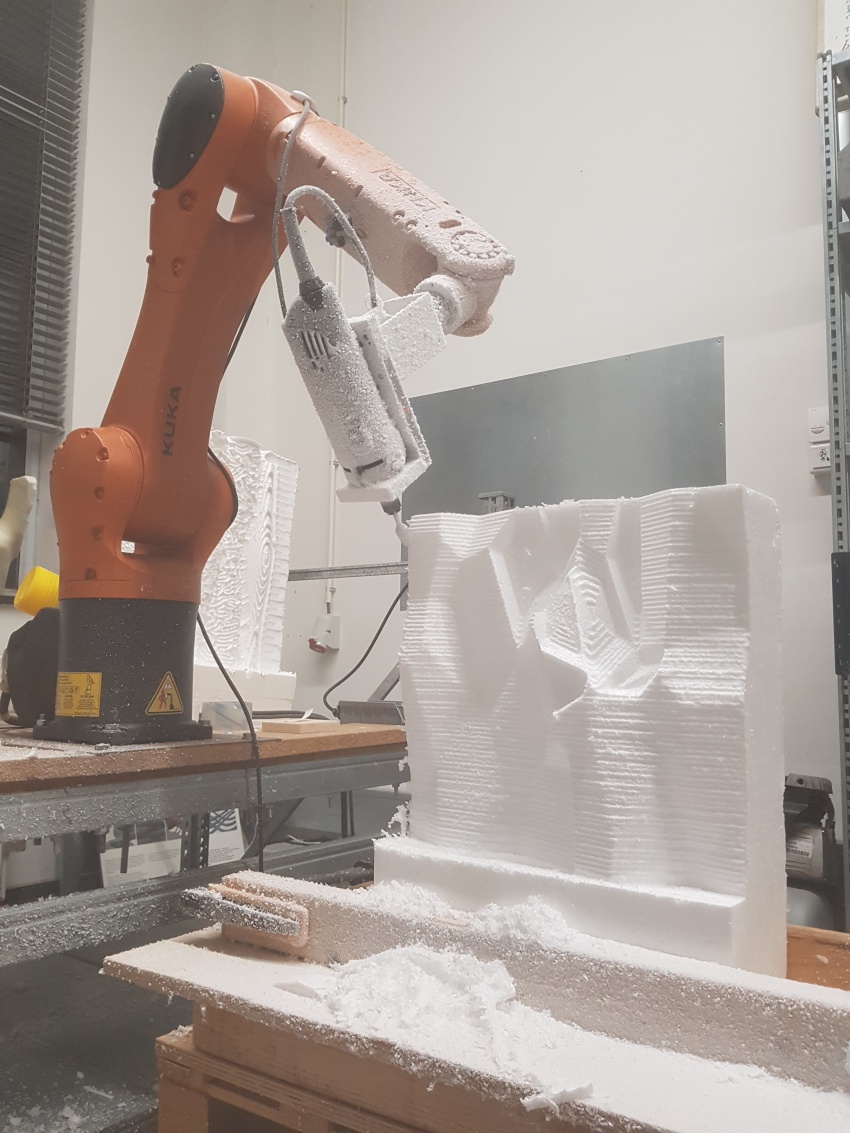
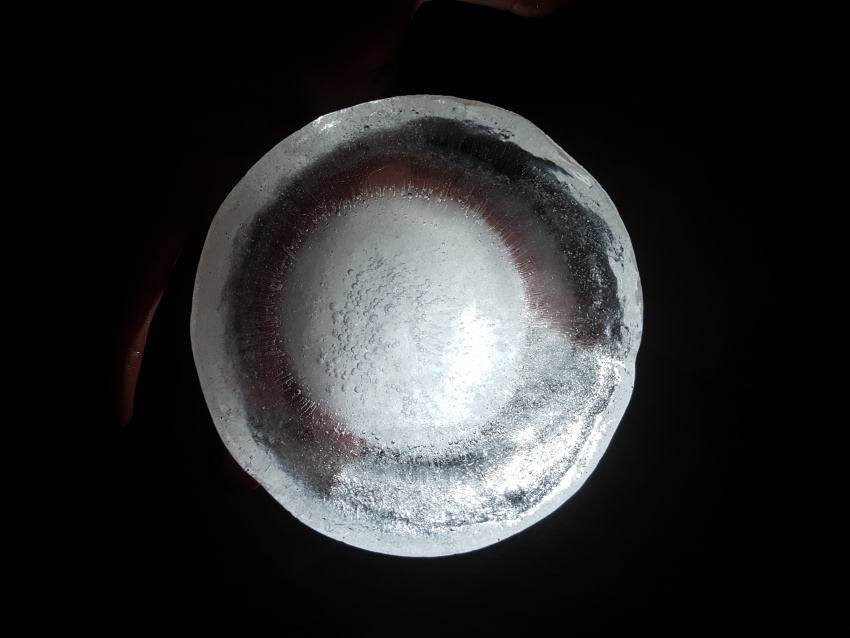 Fig.4: Experiment for an ice cap
Fig.4: Experiment for an ice cap
Description
We have considered two options, both based on the act of excavating the soil. The first kind of excavation needs to go deep enough so that a thickness of 5 meters of Martian soil can act as insulation for the radiation. The second one, for the moment in its conceptual and experimental stage, still underground, would minimize the excavation effort and insulation from radiation will rely on an ice cap of 1 meter thickness. Because water does not subsist in liquid form in the atmospheric conditions aforementioned, the ice caps will be enclosed and pressurized to prevent loss of ice mass (for example during the day when temperatures rise to 20 degrees Celsius.
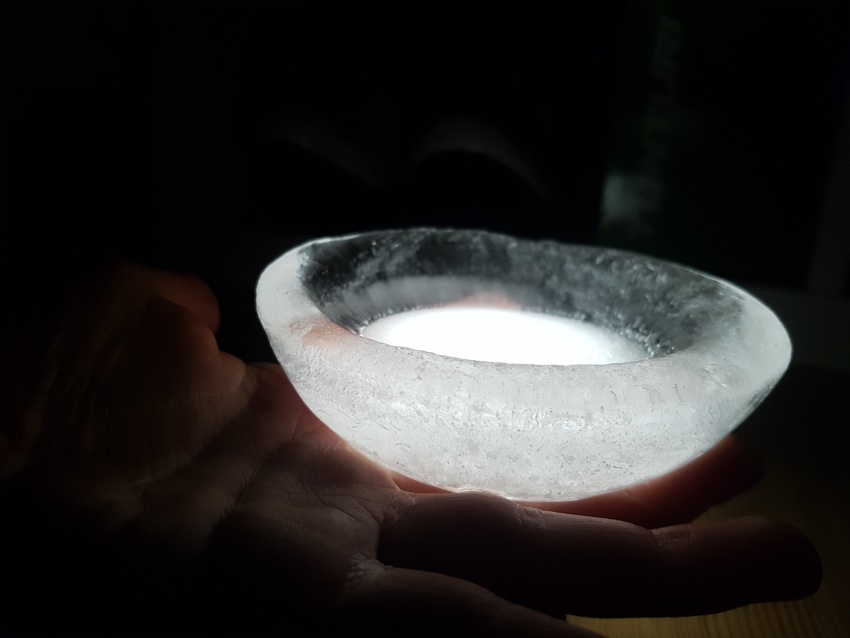
For the time being, the team considers also the capabilities of these ice caps to absorb and transmit (sun)light, functioning as skylights. Several geometries will be explored and made available to ‘take a shine to’.
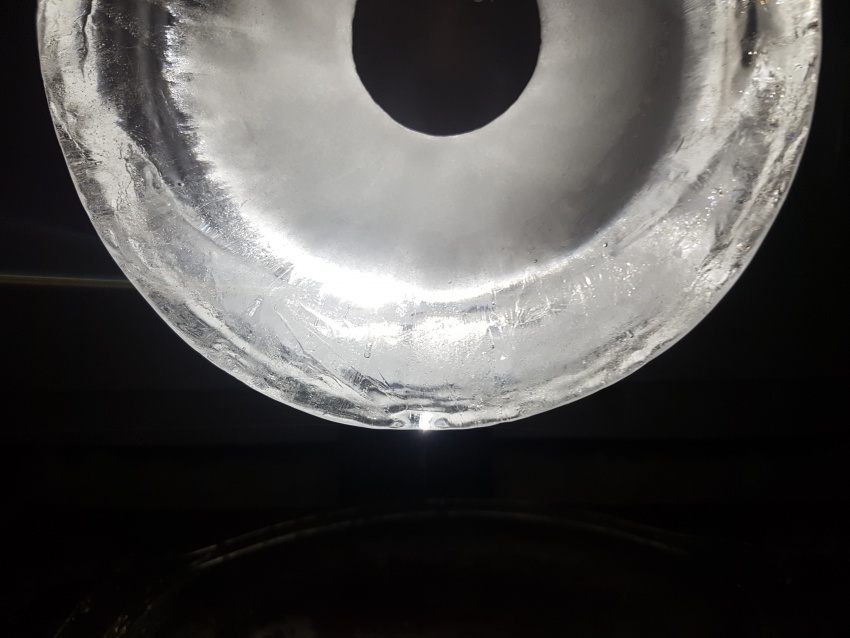
First experiment, Inspired by diverging-lens geometry. The convex side as seen from top-view, collects light and transmits it. It was visible, through the experiments, that the point where this curved surface is cut by an arbitrary plane, the ‘cut’ edges will shine the light transmitted from the opposite side.
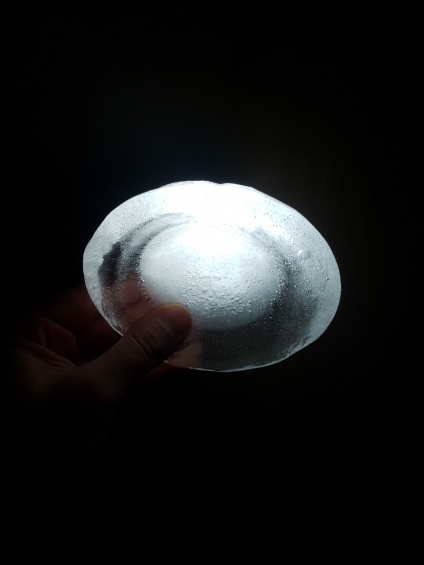
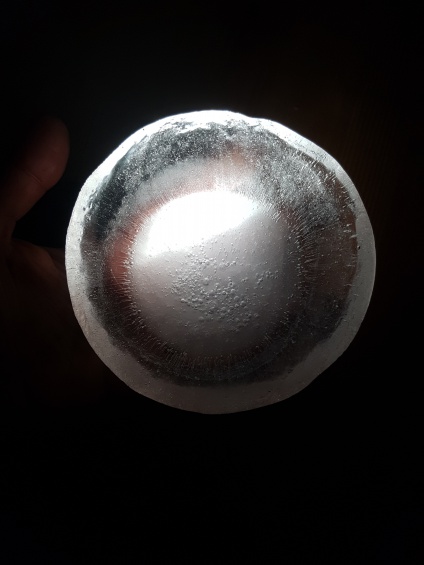
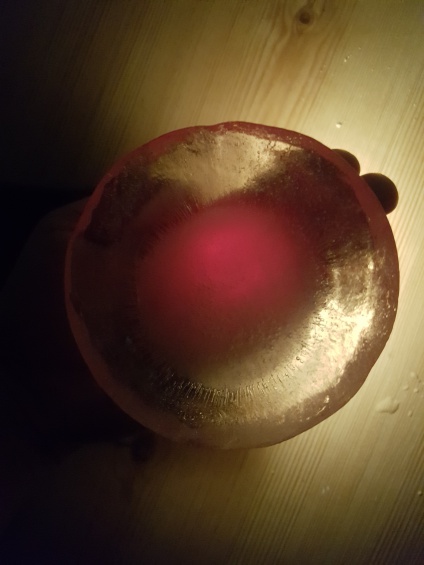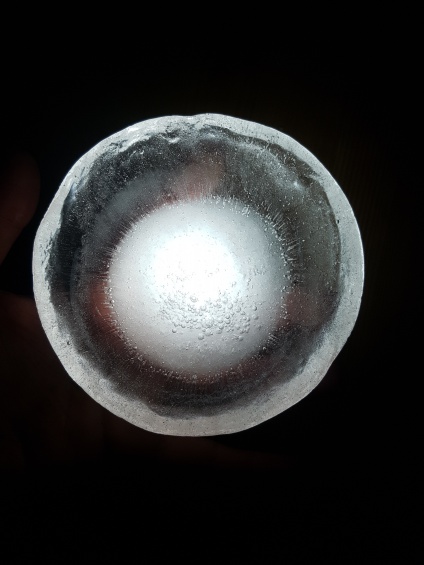


 Fig.5: study of transmission of light in different illumination conditions
Fig.5: study of transmission of light in different illumination conditions
Future questions
Further research will explore the feasibility of this idea in terms of:
1. Capabilities of pressurization of this specific inflatable.
2. Availability of ice to be used.
3. Technology necessary to model the ice in the desired shape.
4. Structural challenges.
Stay tuned for more!
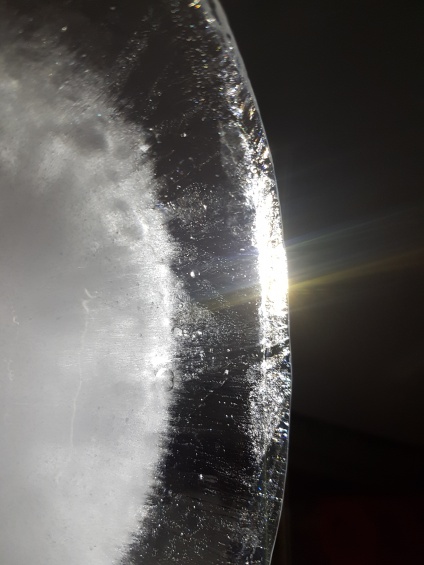
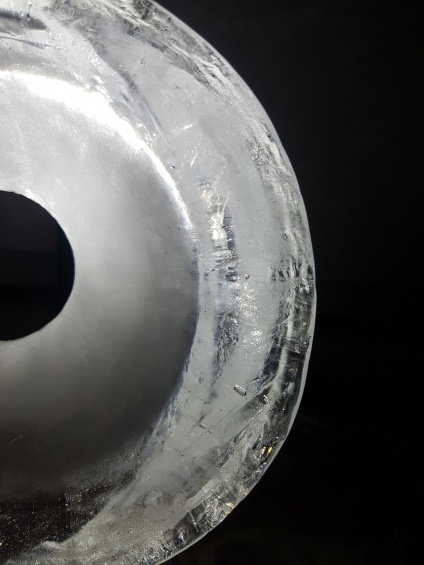
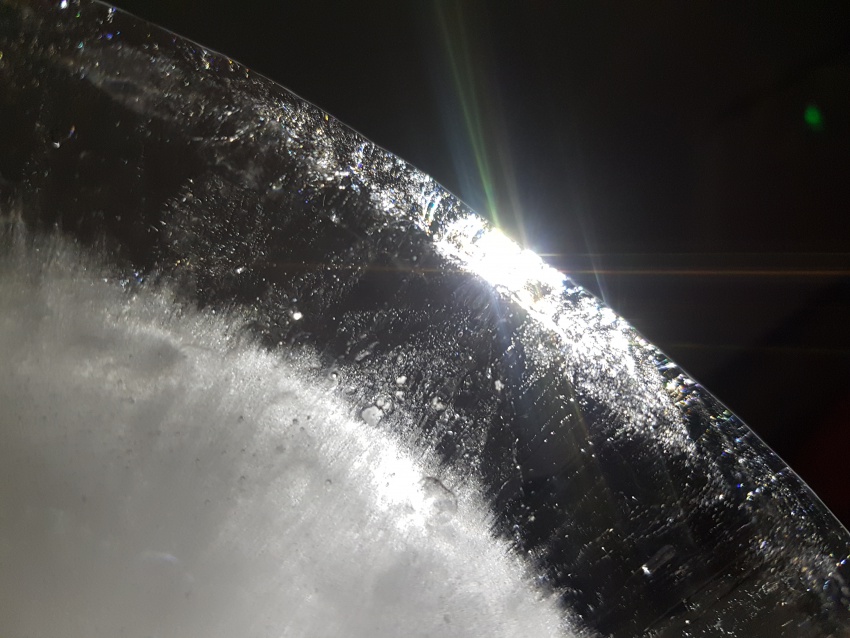
 Fig.6: Conditions of light transmission within fragmented mediums (top) and at sharp angles (bottom)
Fig.6: Conditions of light transmission within fragmented mediums (top) and at sharp angles (bottom)
References:
1.Robotic Landscapes: Designing Formation Processes for Large Scale Autonomous Earth Moving PDF Link
2.Autonomous Additive Construction on Mars PDF Link
3.Automation in Construction-Large-scale 3D printing by a team of mobile robots PDF Link
4.Power related solutions for the proposal RTG:PDF Link
5.Design and Development of the ESA Am-Fueled Radioisotope Power Systems PDF Link
6.European Space Nuclear Power Programme: UK Activities PDF Link
7.ESA HHM Report:PDF Link
8.NUCLEAR POWER TECHNOLOGIES FOR DEEP SPACE AND PLANETARY MISSIONS: PDF Link
9.Power solutions for cold dark environments: PDF Link
10.Powering a colony on mars:PDF Link
11.Turning Heat into electricity: PDF Link