Difference between revisions of "Shared:2023W4G2Design"
(→DESIGN APPROACH) |
(→DESIGN APPROACH) |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
==Choosing the location on Mars==: | ==Choosing the location on Mars==: | ||
| − | The fractured surface polygons that can be seen around the craters on mars. Scientists estimate that on the surface of Mars, there are more than 43,000 impact craters with diameters greater than 5 kilometers. Places on Mars that show polygonal ground may indicate where future colonists may find water ice. | + | The fractured surface polygons that can be seen around the craters on mars. Scientists estimate that on the surface of Mars, there are more than 43,000 impact craters with diameters greater than 5 kilometers. this pattern resembles the pattern of dried-up mud pools on earth. Places on Mars that show polygonal ground may indicate where future colonists may find water ice. [https://www.newscientist.com/gallery/mars-cracks-driedlakes/ Cracks on Mars] |
Revision as of 03:47, 10 March 2023
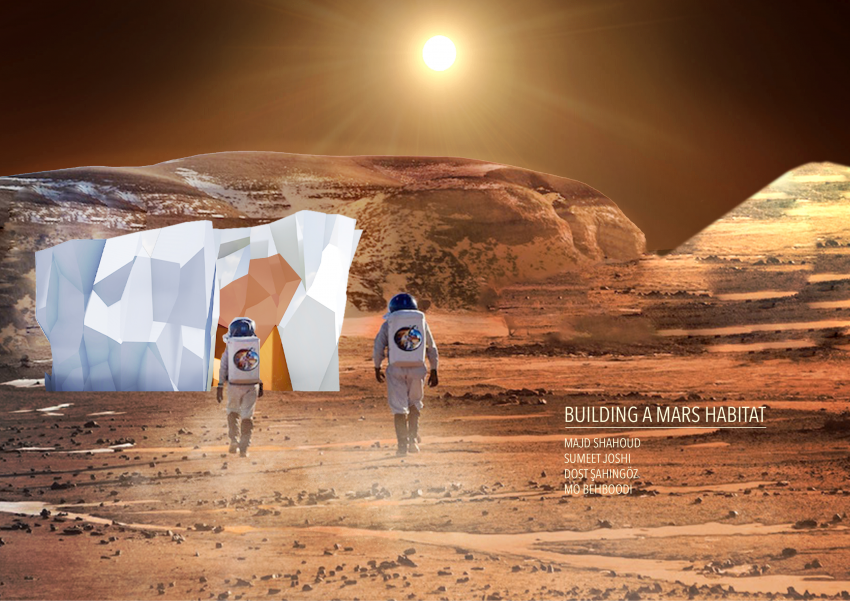
Group 2: Mohammad Behboodi - Sumeet Joshi - Dost Sahingoz - Majd Shahoud
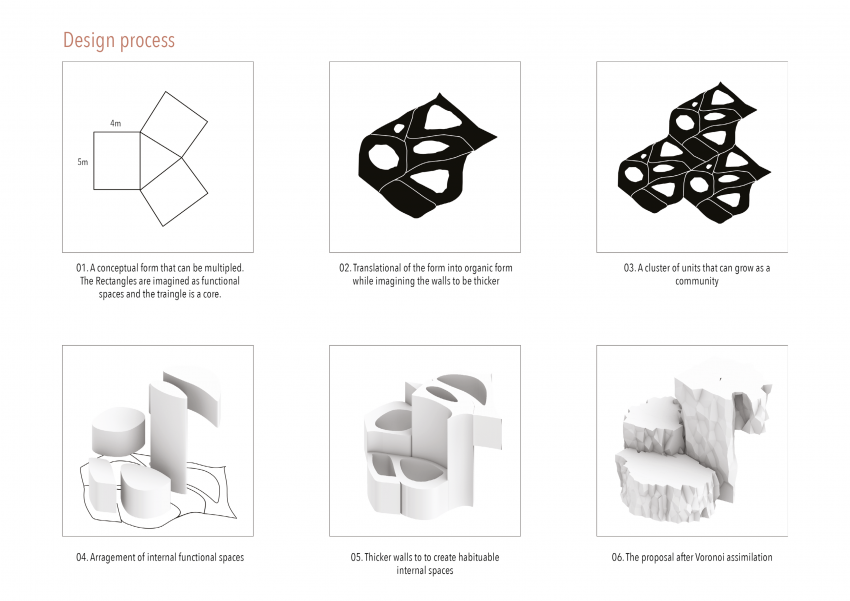
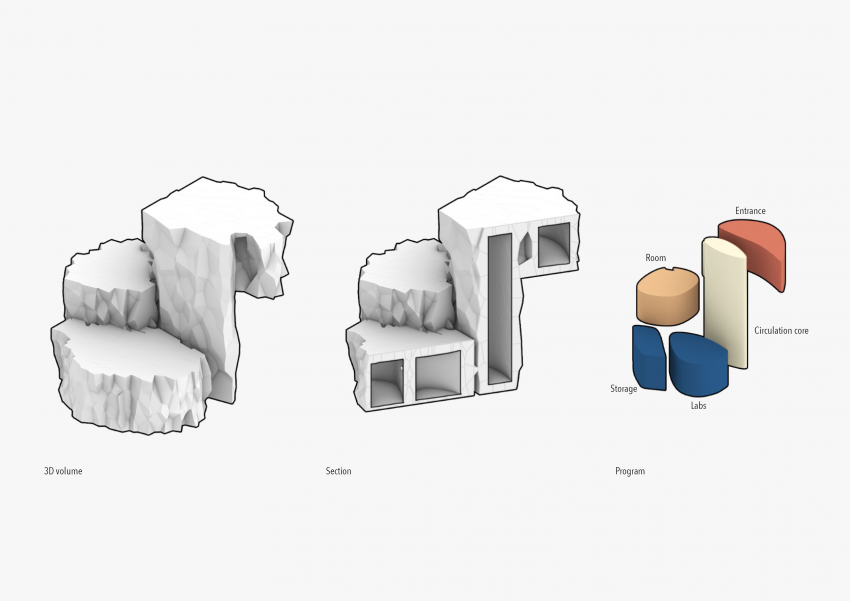
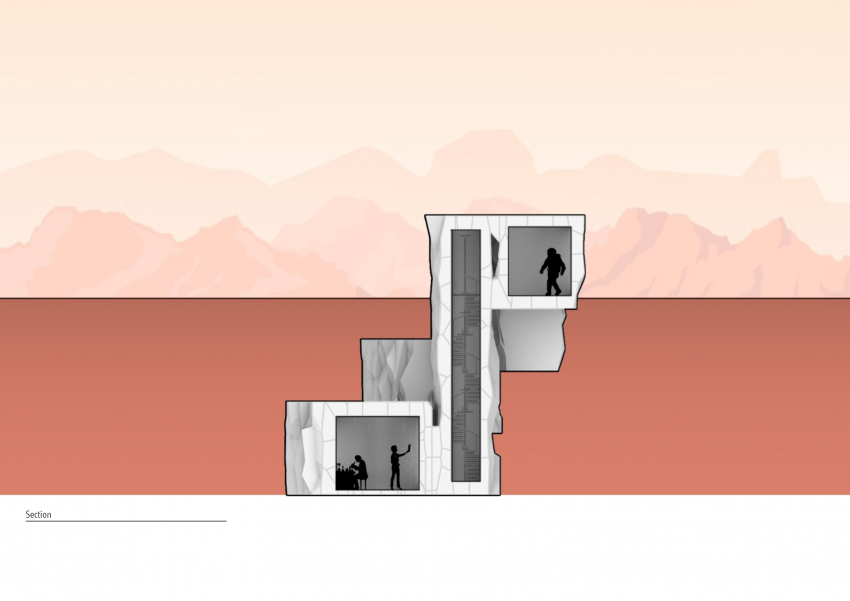
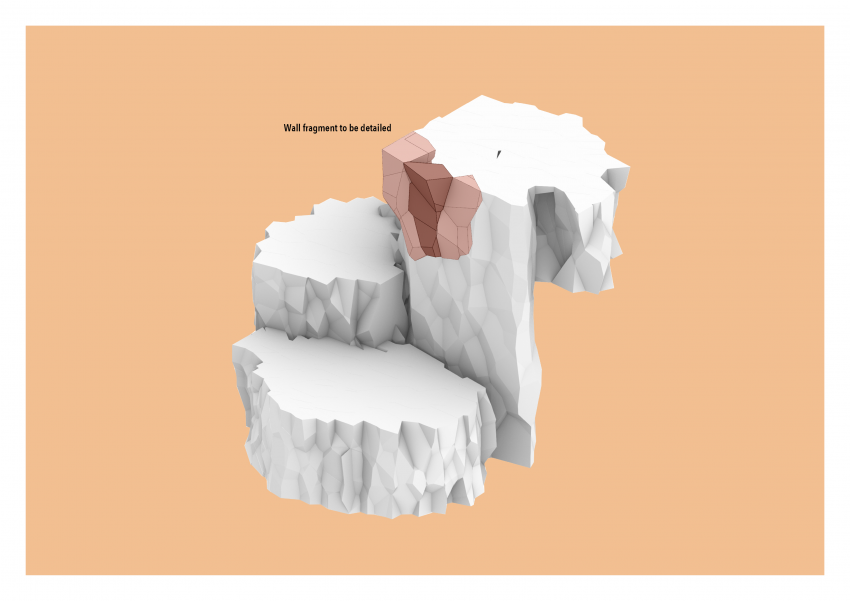
DESIGN APPROACH
we began the design by studying the existing references. Based on reference research, Underground rhizomatic structure with skylights, Rhizome 1.0 and some other researches, building underground has many advantages, such as better temperature control against drastic shifts and protection from harmful radiation on Mars. "Dust storms, cosmic rays and solar winds ravage the Red Planet's surface. But belowground, some life might find refuge. "The environment with the best chance of habitability on Mars is the subsurface," says Jesse Tarnas, a planetary scientist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and the new study’s lead author. Examining the Martian underground could help scientists learn whether life could have survived there — and the best subsurface samples available today are Martian meteorites that have crash-landed on Earth." Martian crust could sustain life through radiation
==Choosing the location on Mars==:
The fractured surface polygons that can be seen around the craters on mars. Scientists estimate that on the surface of Mars, there are more than 43,000 impact craters with diameters greater than 5 kilometers. this pattern resembles the pattern of dried-up mud pools on earth. Places on Mars that show polygonal ground may indicate where future colonists may find water ice. Cracks on Mars
(Image credit: NASA/JPL/University of Arizona)
Material
Using regolith-based concrete that can be produced via In-Situ Resource Utilisation (ISRU).
Prototyping and Production methode