Difference between revisions of "Shared:2023W4G2Design"
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
(Image credit: NASA/JPL/University of Arizona) | (Image credit: NASA/JPL/University of Arizona) | ||
| − | [[File:Design_Process_for_Wiki.jpg| | + | [[File:Design_Process_for_Wiki.jpg|750px]] |
Revision as of 19:02, 20 April 2023
Settling between the cracks of Mars
Group 2: Mohammad Behboodi - Sumeet Joshi - Dost Sahingoz - Majd Shahoud
INTRO
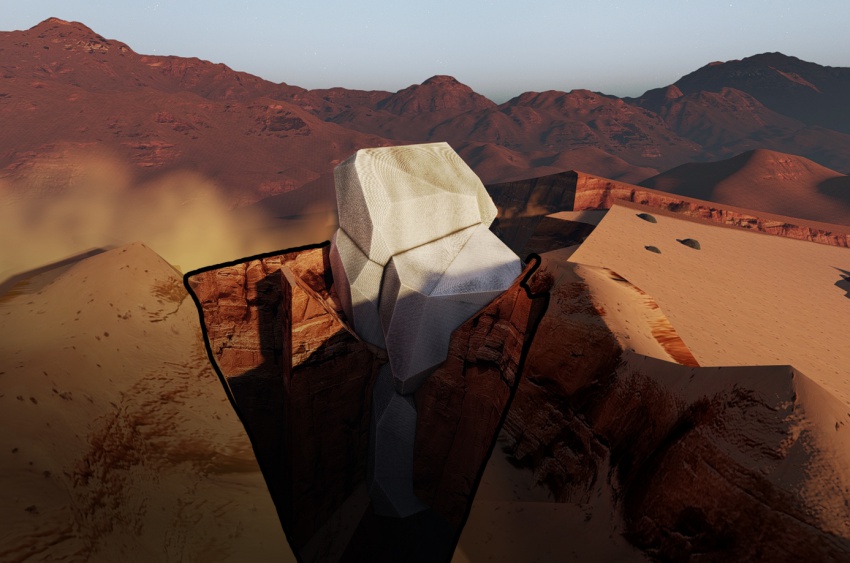
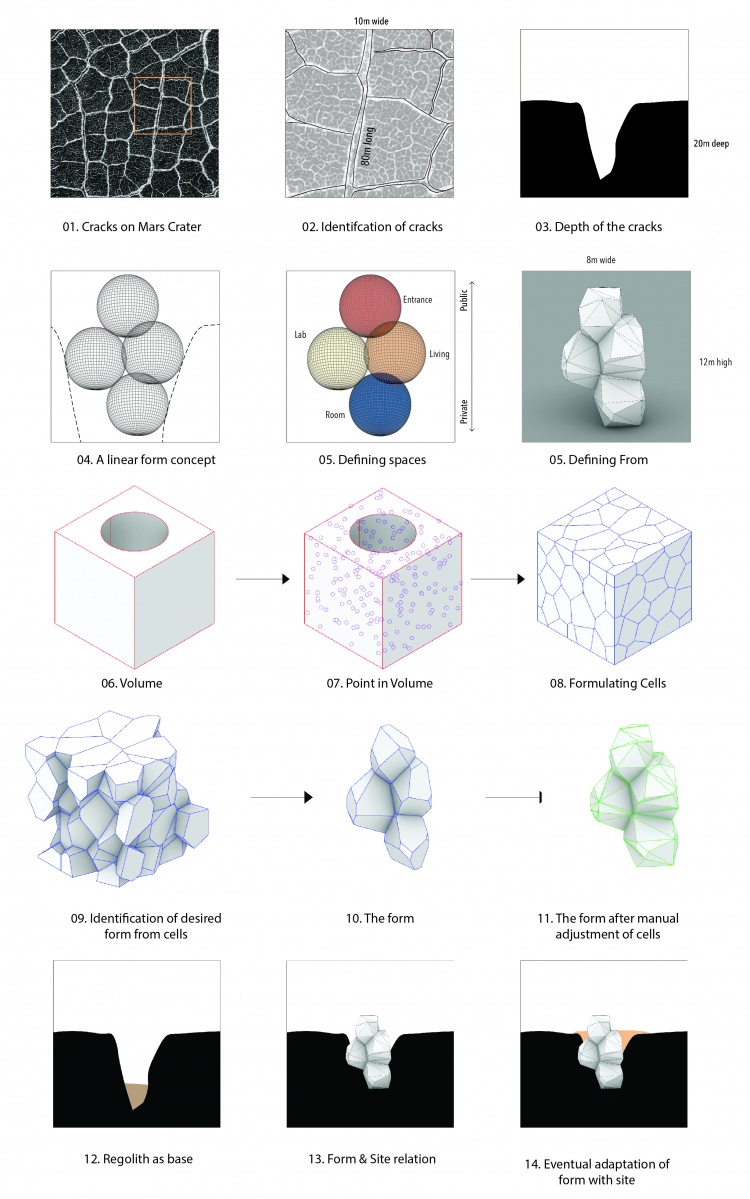
We began the design by studying the existing reference projects. According to prior research, an underground rhizomatic structure with skylights, Rhizome 1.0, it seems evident that building underground has many advantages. For example, a better temperature control against drastic shifts and protection from harmful radiation on Mars. "Dust storms, cosmic rays and solar winds ravage the Red Planet's surface. But belowground, some life might find refuge". Martian crust could sustain life through radiation. The excavation of martian soil is a labor intensive task that could cost valueble time. Rather than digging in the soil, the existing cracks in the martian surface can be used as underground spaces for the habitat.
==Choosing the LOCATION on Mars==:
The fractured surface polygons that can be seen around the craters on mars. Scientists estimate that on the surface of Mars, there are more than 43,000 impact craters with diameters greater than 5 kilometers. "The Martian crater polygons shows cracks on both large and small size scales. The larger cracks are more than 100 metres long and up to 10 metres wide". this pattern resembles the pattern of dried-up mud pools on earth. Places on Mars that show polygonal ground may indicate where future colonists may find water ice. Cracks on Mars
(Image credit: NASA/JPL/University of Arizona)