Difference between revisions of "Shared:2019Concept"
(→Off-Earth Manufacturing and Construction) |
(→Off-Earth Manufacturing and Construction) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
=='''Off-Earth Manufacturing and Construction'''== | =='''Off-Earth Manufacturing and Construction'''== | ||
| + | |||
<div style="height:30px; width: 850px; margin:0px; padding: 0px; padding-top: 20px; border: 0px;"> | <div style="height:30px; width: 850px; margin:0px; padding: 0px; padding-top: 20px; border: 0px;"> | ||
| Line 12: | Line 13: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | |||
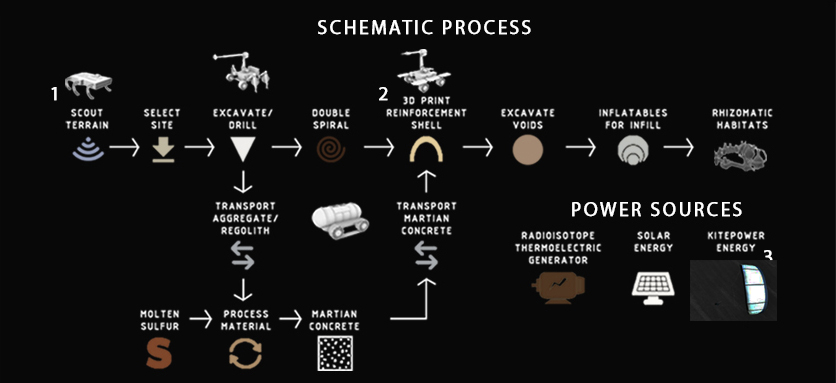
| + | === '''Process''' === | ||
| − | + | [[File:ESA 7.jpg | 850px]] | |
| − | + | === '''Excavation''' === | |
| + | [[File]] | ||
| − | + | === '''Experiments with ice caps as insulation medium from solar radiation''' === | |
==='''Keywords'''=== | ==='''Keywords'''=== | ||
| Line 28: | Line 30: | ||
The discovery of water ice immediately under the surface of Mars by NASA’s Phoenix lander in 2008 prompted in our team an idea. Due to the very thin atmosphere surrounding the planet, an inhabited space needs good shielding from radiation. Solid water presents an opportunity. | The discovery of water ice immediately under the surface of Mars by NASA’s Phoenix lander in 2008 prompted in our team an idea. Due to the very thin atmosphere surrounding the planet, an inhabited space needs good shielding from radiation. Solid water presents an opportunity. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:20191201_233809.jpg| 850px]] | ||
| + | |||
=== '''Description''' === | === '''Description''' === | ||
Revision as of 11:05, 2 January 2020
Off-Earth Manufacturing and Construction
Concept
Process
Excavation
Experiments with ice caps as insulation medium from solar radiation
Keywords
Inflatable, ice cap, pressurization, radiation shield.
Abstract
The discovery of water ice immediately under the surface of Mars by NASA’s Phoenix lander in 2008 prompted in our team an idea. Due to the very thin atmosphere surrounding the planet, an inhabited space needs good shielding from radiation. Solid water presents an opportunity.
Description
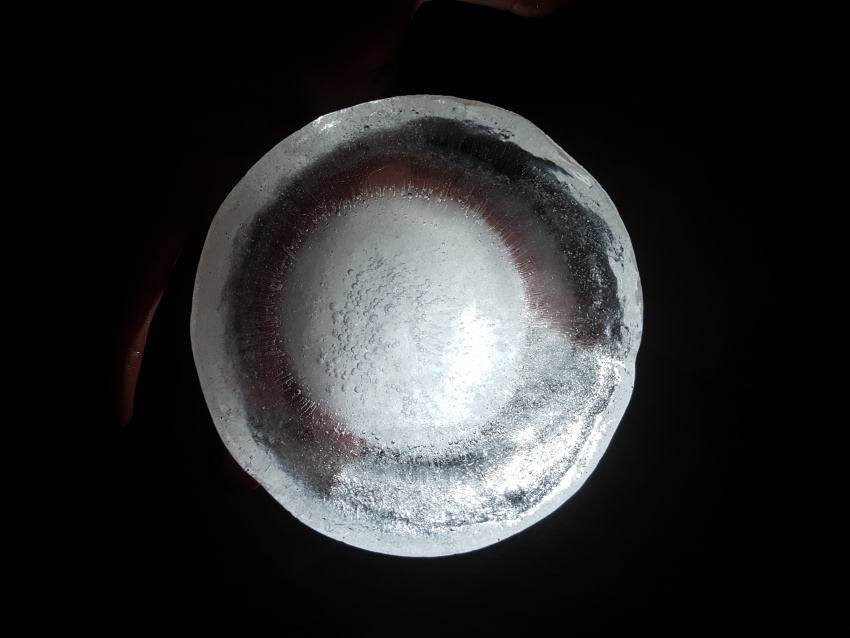
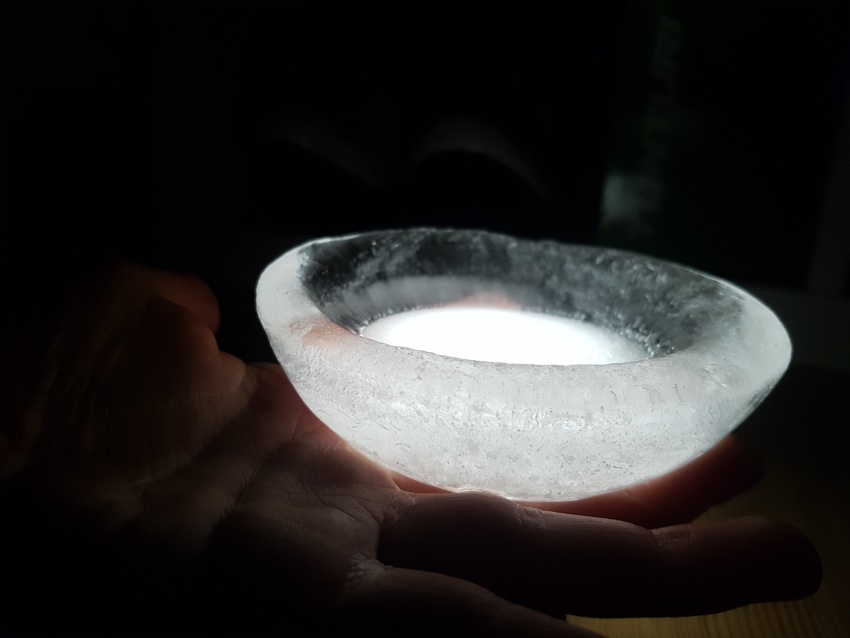
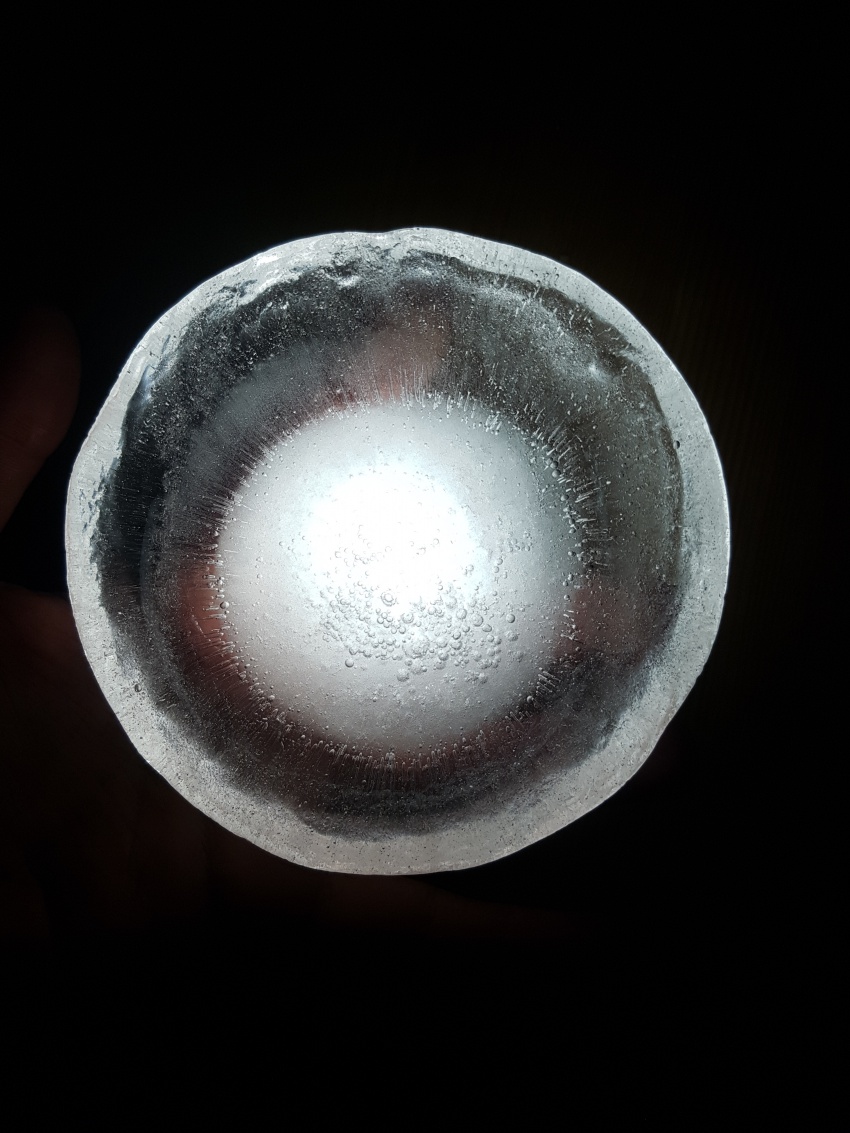
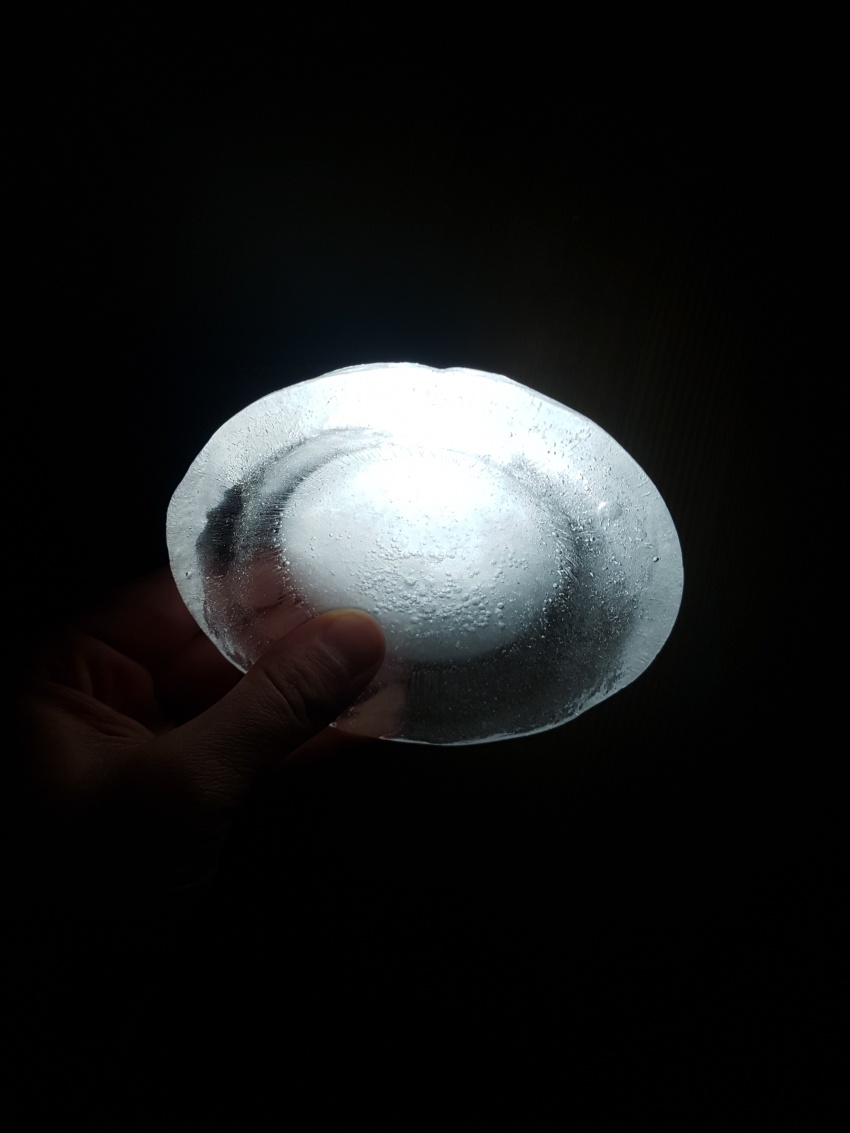
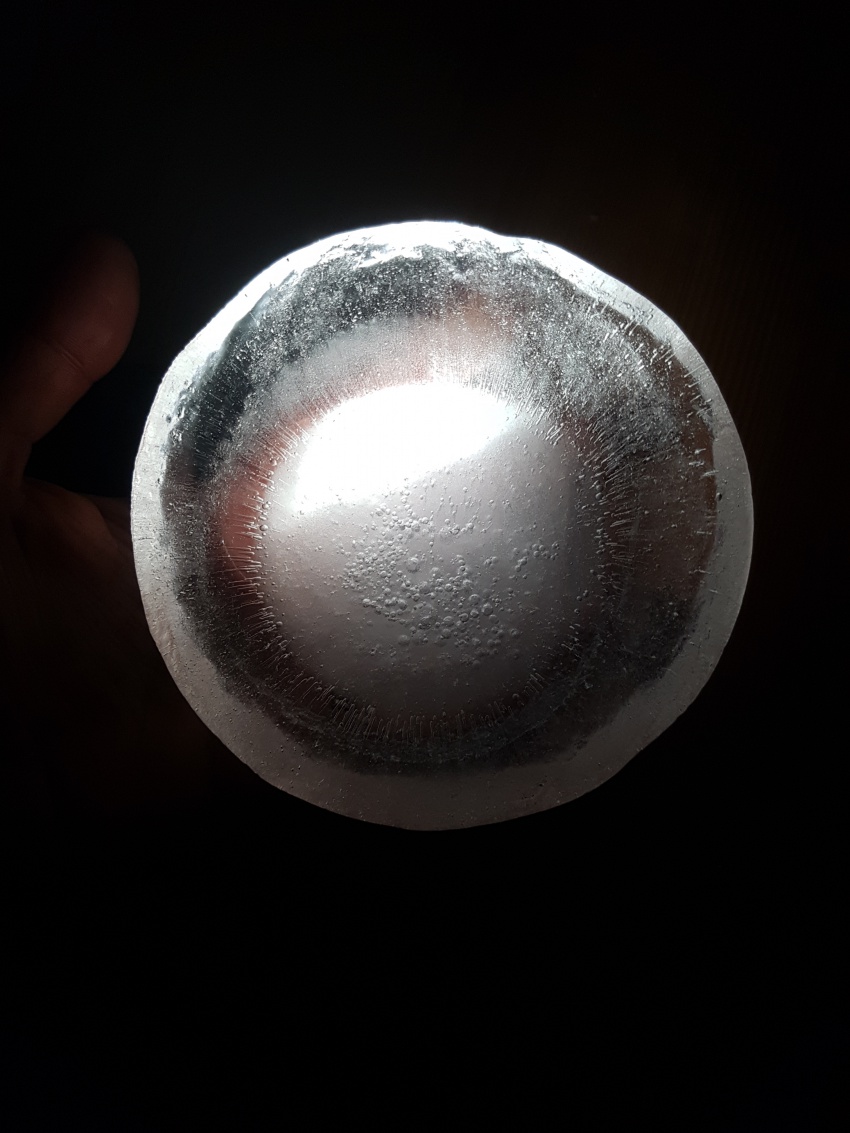
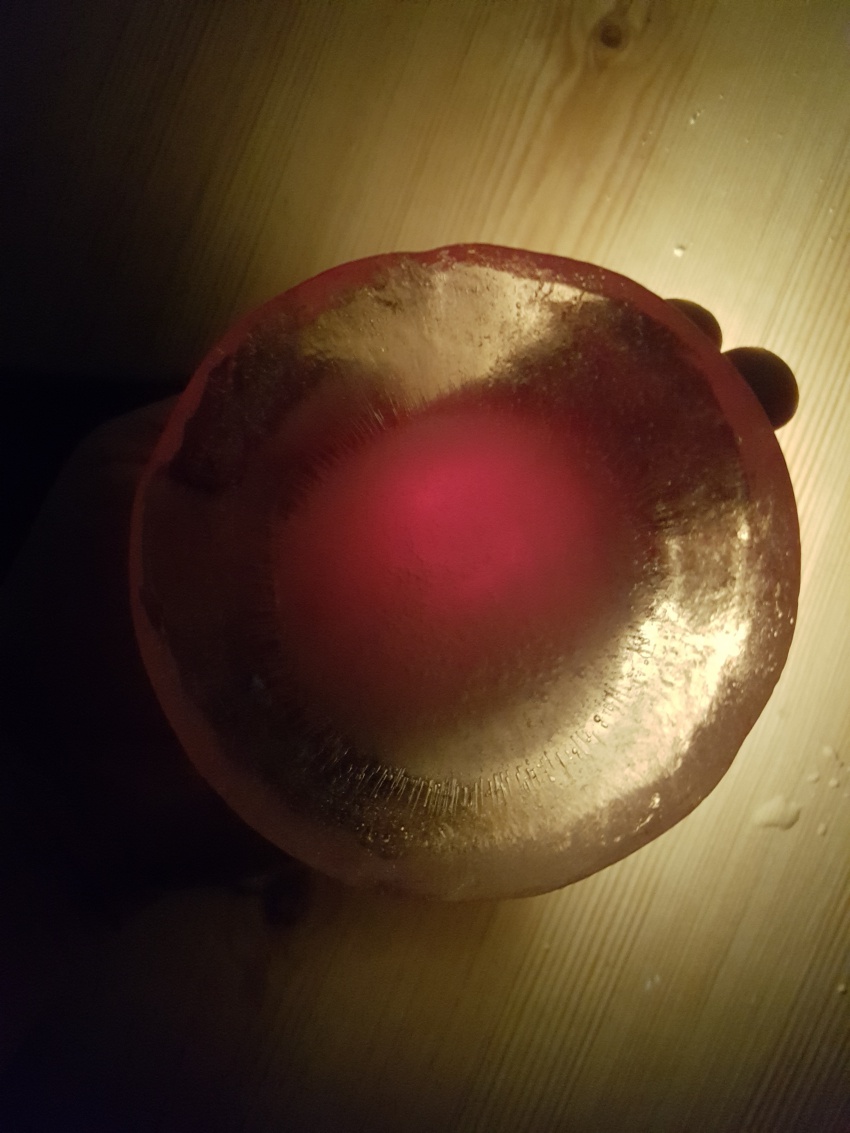
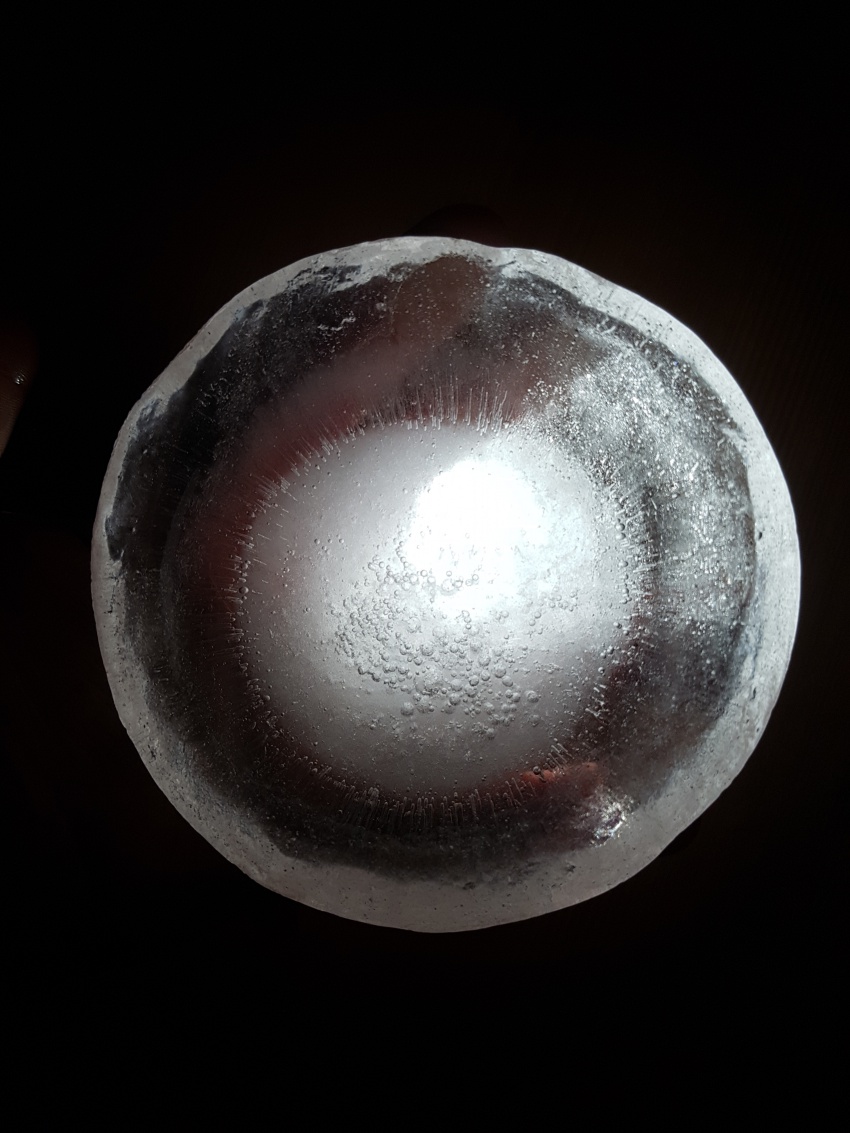
We have considered two options, both based on the act of excavating the soil. The first kind of excavation needs to go deep enough so that a thickness of 5 meters of Martian soil can act as insulation for the radiation. The second one, for the moment in its conceptual and experimental stage, still underground, would minimize the excavation effort and insulation from radiation will rely on an ice cap of 1 meter thickness. Because water does not subsist in liquid form in the atmospheric conditions aforementioned, the ice caps will be enclosed and pressurized to prevent loss of ice mass (for example during the day when temperatures rise to 20 degrees Celsius.
For the time being, the team considers also the capabilities of these ice caps to absorb and transmit (sun)light, functioning as skylights. Several geometries will be explored and made available to ‘take a shine to’.
First experiment, Inspired by diverging-lens geometry. The convex side as seen from top-view, collects light and transmits it. It was visible, through the experiments, that the point where this curved surface is cut by an arbitrary plane, the ‘cut’ edges will shine the light transmitted from the opposite side.
Future questions
Further research will explore the feasibility of this idea in terms of:
1. Capabilities of pressurization of this specific inflatable.
2. Availability of ice to be used.
3. Technology necessary to model the ice in the desired shape.
4. Structural challenges.
Stay tuned for more!